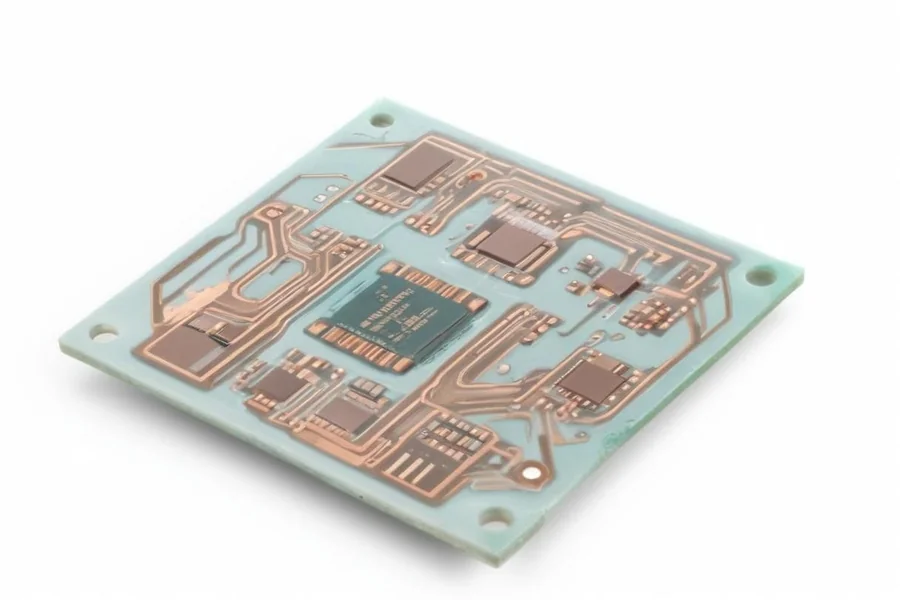
Ceramic PCBs are rapidly becoming the foundation for next-generation electronics, thanks to their exceptional thermal and electrical performance. Unlike standard FR4 circuit boards, ceramic PCBs are made using materials like alumina (Al₂O₃), aluminum nitride (AlN), or beryllium oxide (BeO), which offer remarkable durability, high thermal conductivity, and electrical insulation. These characteristics make ceramic PCBs a top choice for demanding applications across industries such as aerospace, medical, LED lighting, automotive, and telecommunications.
Advantages of Ceramic PCB Technology
The primary advantage of ceramic PCB lies in its outstanding heat dissipation capabilities. In high-power environments, conventional PCBs often suffer from thermal stress and warping, leading to failure over time. Ceramic substrates remain stable even at elevated temperatures, allowing them to handle intensive applications such as power amplifiers, automotive electronics, and industrial control systems. With better thermal conductivity, ceramic boards can maintain device performance while reducing the need for additional heat sinks or cooling mechanisms.
Another standout feature is the ability to support miniaturized, high-density designs. The mechanical strength and dimensional stability of ceramic materials enable precise, compact circuitry, which is essential for devices like hearing aids, implantable medical tools, and high-frequency RF modules. Engineers can also use thinner dielectric layers without compromising insulation, allowing for shorter signal paths and lower electrical loss.
Performance in Harsh Environments
Ceramic PCBs offer superior reliability in extreme environments. Their inherent resistance to moisture, corrosion, and chemicals makes them ideal for mission-critical applications in oil rigs, aerospace systems, and military-grade electronics. Additionally, they do not require conformal coating or additional protection to maintain their function in tough conditions, reducing production complexity and cost.
Electrical Properties for High-Frequency Applications
From a signal transmission standpoint, ceramic PCBs excel at preserving signal integrity, especially in high-frequency applications. The uniform dielectric constant of ceramic substrates ensures minimal signal distortion and interference, a critical requirement for communication devices, radar systems, and satellite equipment. These boards also exhibit low signal loss and low parasitic capacitance, further enhancing their suitability for advanced RF and microwave circuits.
Manufacturing Techniques and Material Options
Ceramic PCBs are typically manufactured using processes like Direct Bonded Copper (DBC), Direct Copper Bonding (DCB), or Low-Temperature Co-fired Ceramic (LTCC). These methods ensure excellent adhesion between the copper traces and ceramic substrate, resulting in durable and high-performance PCBs capable of handling thermal cycles and mechanical stress. Among the various substrate materials, alumina is commonly used for general applications, while AlN is preferred for high-power systems due to its higher thermal conductivity.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Benefits
Beyond their technical performance, ceramic PCBs also contribute to energy-efficient electronics. By naturally dissipating heat without relying on external cooling, these boards reduce the energy load required to regulate device temperatures. This not only extends the lifespan of components but also supports sustainable product design—a growing consideration for manufacturers striving to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact.
Versatility Across Industries
Ceramic PCBs are used in a wide array of applications. In the medical field, they are found in ultrasound equipment, pacemakers, and lab instrumentation. In automotive electronics, they support engine control units and LED lighting systems. The telecommunications sector leverages them in antenna modules and RF devices. Their ability to adapt to various formats, including multilayer and hybrid constructions, makes them suitable for both rigid and compact flexible designs.
Market Demand and Future Outlook
As industries evolve toward faster, smaller, and more powerful electronics, the demand for ceramic PCBs is expected to grow rapidly. The rollout of 5G networks, increased adoption of electric vehicles, and advancements in medical diagnostics are all driving the need for boards that offer high thermal stability, compactness, and signal integrity. Ceramic PCBs are uniquely equipped to meet these challenges, ensuring long-term reliability and innovation across critical applications.
Work with a Trusted Ceramic PCB Manufacturer
To unlock the full benefits of ceramic PCBs, it is essential to collaborate with a manufacturing partner who understands the complexities of this technology. Whether you need prototype development or full-scale production, working with a supplier experienced in advanced materials and precise fabrication is vital. If you’re seeking a reliable ceramic PCB manufacturer, choose a company with a proven track record in high-performance, customized PCB solutions. A trusted ceramic PCB manufacturer will ensure quality, performance, and consistency across every board they produce—helping your products succeed in today’s competitive electronics market.